-40%
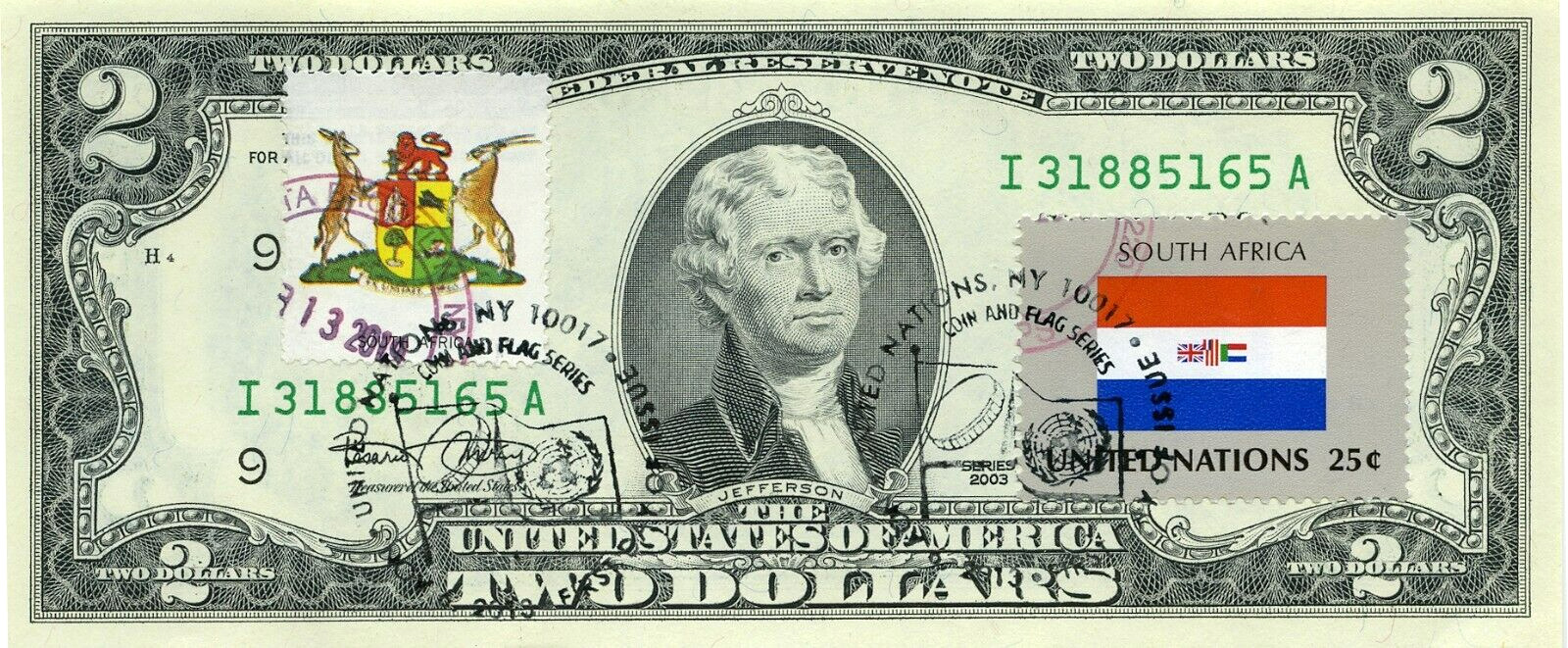
2003 STAMPS CANCELED FLAG THE UN FROM SOUTH AFRICA LUCKY MONEY VALUE 0
$ 158.4
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
2003 STAMPS CANCELED FLAG THE UN FROM SOUTH AFRICA LUCKY MONEY VALUE 0S/N I 31885164 A
GEM UNC
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa.
It is bounded to the south by 2,798 kilometers (1,739 mi) of coastline that stretches along the South Atlantic and Indian Ocean; to the north by the neighboring countries of Namibia, Botswana, and Zimbabwe.
and to the east and northeast by Mozambique and Eswatini. It also completely enclaves Lesotho.
It is the southernmost country on the mainland of the Old World,
and the second-most populous country located entirely south of the equator, after Tanzania.
South Africa is a biodiversity hotspot, with unique biomes,
plant and animal life. With over 62 million people, the country is the world's 23rd-most
populous nation and covers an area of 1,221,037 square kilometers (471,445 square miles).
Pretoria is the administrative capital, while Cape Town, the seat of Parliament, is the legislative capital.
Bloemfontein has traditionally been regarded as the judicial capital.
The Constitutional Court, the country's highest court, is located in Johannesburg.
About 80% of the population are Black South Africans.
The remaining population consists of Africa's largest communities of European (White South Africans),
Asian (Indian South Africans and Chinese South Africans), and multiracial (Colored South Africans) ancestry.
South Africa is a multiethnic society encompassing a wide variety of cultures,
languages, and religions.
Its pluralistic makeup is reflected
in the Constitution's recognition of 12 official languages, the fourth-highest number in the world.
According to the 2011 census, the two most spoken first languages are Zulu (22.7%) and Xhosa (16.0%).
The next two are of European origin; Afrikaans (13.5%), developed from Dutch,
serves as the first language of most Colored and White South Africans, while English (9.6%)
reflects the legacy of British colonialism and is commonly used in public and commercial life.
Regular elections have been held for almost a century in the country. However, the vast majority of Black South Africans were not enfranchised until 1994.
During the 20th century, the black majority sought to claim more rights from the dominant white minority,
which played a large role in the country's recent history and politics.
The National Party imposed apartheid in 1948, institutionalizing previous racial segregation.
After a largely non-violent struggle by the African National Congress and other
anti-apartheid activists both inside and outside the country, the repeal of discriminatory laws began in the mid-1980s.
Since 1994, all ethnic and linguistic groups have held political representation
in the country's liberal democracy, which comprises a parliamentary republic and nine provinces.
South Africa is often referred to as the "rainbow nation"
to describe the country's multicultural diversity, especially in the wake of apartheid.
According to the 2023 V-Dem Democracy indices, South Africa
is ranked the 51st electoral democracy worldwide and the 3rd electoral democracy in Africa.
South Africa is a middle power in international affairs;
it maintains significant regional influence and is a member of both the Commonwealth of Nations and the G20.
It is a developing country, ranking 110th on the Human Development Index,
the 7th highest on the continent.
South Africa is the only African nation to legislate same-sex marriage.
It has been classified by the World Bank as a newly industrialized country and has the largest and most industrialized, technologically advanced economy in Africa overall, as well as the 38th-largest economy in the world.
South Africa has the most UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Africa.
Since the end of apartheid, government accountability and quality of life have substantially improved.
However, crime, poverty, and inequality remain widespread, with about 40% of the total population being unemployed as of 2021, while some 60% of the population lived below the poverty line and a quarter lived below .15 a day.
Having the highest Gini coefficient of 63.0,
South Africa is considered to be one of, if not the most, unequal countries in the world.